|
||||||||||||
| 购买进口仪器、试剂和耗材——就在始于2001年的毕特博生物 www.bitebo.com |
巨噬细胞是在宿主防御和炎症中起重要作用的一类先天免疫细胞。单核细胞衍生的巨噬细胞存在于全身的许多组织中。巨噬细胞具有高度的可塑性,可在不同的生理或病理环境中极化形成具有不同功能的特殊亚型。存在于肿瘤中的巨噬细胞通常被称作为肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)。动物模型及临床研究表明,TAMs以各种方式,例如生成促血管生成因子、免疫调控和组织重塑促进了肿瘤进展及转移。肿瘤衍生分子,例如IL-4可诱导巨噬细胞独特的状态促进肿瘤生长。但目前对于TAM发挥功能的潜在机制仍不清楚。 近期的一些研究显示,巨噬细胞是通过生成一些促肿瘤细胞因子来促进肿瘤发生。通常,促炎细胞因子生成处于几条信号通路的紧密控制之下,nf-kb在其中充当了中心调控因子。NF-kB信号负向调控因子例如NLRP12和CYLD发生缺陷,可导致对结肠炎症过敏及肿瘤发生。在以往的研究中,军事医学科学院的研究人员曾报告称发现CUEDC2调控了NF-kB信号,表明它有可能是一个重要的炎症调控分子。 发表于2014年5月29日的《Cell Reports》杂志上的一篇文章上,来自军事医学科学院国家生物医学分析中心的研究人员证实CUEDC2是巨噬细胞功能的一个关键调控因子,并且在保护机体对抗结肠炎相关的肿瘤发生中起至关重要的作用。他们发现在巨噬细胞分化过程中CUEDC2表达显著上调,CUEDC2缺陷可导致过度生成促炎细胞因子。在巨噬细胞中CUEDC2水平受到miR-324-5p的调控。他们发现Cuedc2基因敲除(KO)小鼠对于葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的结肠炎更为敏感,巨噬细胞移植结果表明,敏感度增加是由于缺失CUEDC2的巨噬细胞功能失常所导致。 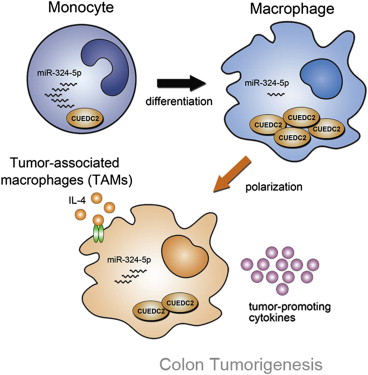 此外,研究人员还发现Cuedc2 KO小鼠更容易形成结肠炎相关的癌症。重要的是,在人类结直肠癌巨噬细胞中几乎无法检测到CUEDC2的表达,这种CUEDC2表达下降与高水平的IL-4和miR-324-5p相关。 这些结果表明了,CUEDC2在调控巨噬细胞功能中发挥了至关重要的作用,并且与结肠炎和结肠肿瘤的形成相关联。新研究为治疗结直肠癌提供了潜在的新靶点。 原文摘要: Dysregulation of the MiR-324-5p-CUEDC2 Axis Leads to Macrophage Dysfunction and Is Associated with Colon Cancer Yuan Chen, Shao-Xin Wang, Rui Mu, Xue Luo, Zhao-Shan Liu, Bing Liang, Hai-Long Zhuo, Xiao-Peng Hao, Qiong Wang, Di-Feng Fang,Zhao-Fang Bai, Qian-Yi Wang, He-Mei Wang, Bao-Feng Jin, Wei-Li Gong, Tao Zhou, Xue-Min Zhang, Qing Xia, Tao Li CUEDC2, a CUE-domain-containing protein, modulates inflammation, but its involvement in tumorigenesis is still poorly understood. Here, we report that CUEDC2 is a key regulator of macrophage function and critical for protection against colitis-associated tumorigenesis. CUEDC2 expression is dramatically upregulated during macrophage differentiation, and CUEDC2 deficiency results in excessive production of proinflammatory cytokines. The level of CUEDC2 in macrophages is modulated by miR- 324-5p. We find that Cuedc2 KO mice are more susceptible to dextran-sodium-sulfate-induced colitis, and macrophage transplantation results suggest that the increased susceptibility results from the dysfunction of macrophages lacking CUEDC2. Furthermore, we find that Cuedc2 KO mice are more prone to colitis-associated cancer. Importantly, CUEDC2 expression is almost undetectable in macrophages in human colon cancer, and this decreased CUEDC2 expression is associated with high levels of interleukin-4 and miR-324-5p. Thus, CUEDC2 plays a crucial role in modulating macrophage function and is associated with both colitis and colon tumorigenesis. |
购买进口仪器、试剂和耗材——就在始于2001年的毕特博生物
www.bitebo.com |
|